Getting Started with Laravel in CodeLobster IDE
In this article, We are going to learn how to getting started with Laravel in CodeLobster IDE. Codelobster helps you to make a local Laravel installation quickly and effortlessly. There is no need to use the command line or download and run VirtualBox and Homestead virtual machine, which is larger than 2 GB.
Prerequisites
Professional programmers use it widely in their projects, so beginners also need to learn Laravel as soon as possible.
For the work we need our IDE and the latest version of XAMPP, which in all respects is suitable for the correct operation of the newest version of the framework. This article uses XAMPP 7.2.12, and we recommend that you install it too.
Launch CodeLobster and go to the main menu Tools -> Preferences -> PHP. Specify the path to the executable file php.exe, in our system, for example, it looks like this - D:/xampp-7.2.12/php/php.exe.
Check php.ini file and make sure you have enabled all the necessary PHP-extensions such as php_bz2, php_curl, php_fileinfo, php_gd2, php_gettext, php_mbstring, php_exif, php_mysqli, php_pdo_mysql, php_pdo_sqlite, php_openssl and php_ftp.
Now everything is ready, let’s run MySQL and Apache servers and start the main work
Installing Laravel in CodeLobster IDE
Go to the main menu Project -> Create Project.
In the dialog box that appears, select the type of the created project Create Empty Laravel Project.
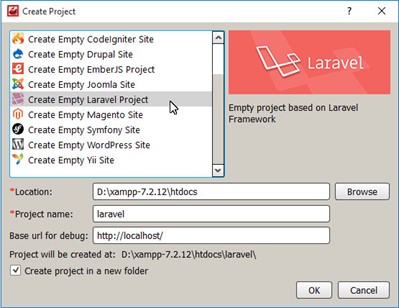
Specify the project name, which we will place in the htdocs folder in the directory with the installed XAMPP.
Enable the option Create project in a new folder and click OK to start the wizard to install the framework.
We have to complete a few steps and enter the elementary settings.
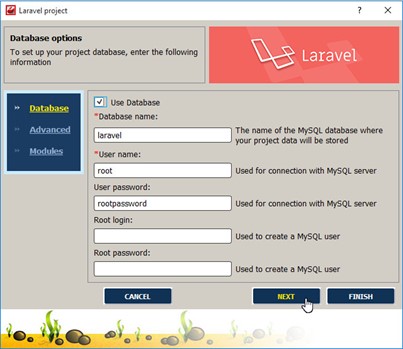
We have to complete a few steps and enter the elementary settings.
In the next dialog box, enter the server name and port. If MySQL is running on the local computer, then nothing needs to be changed at this stage.
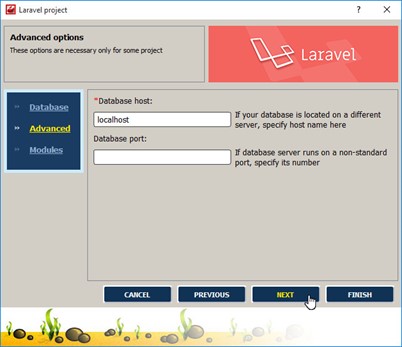
All data entered by us will be automatically saved in the config/database.php file, and later it can be changed manually simply by opening this file in the editor.
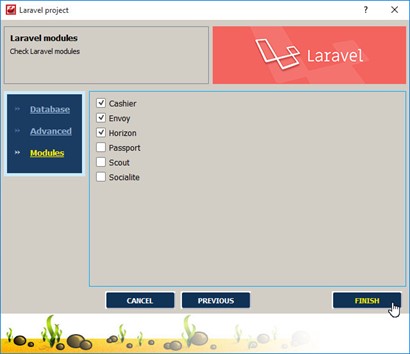
At the next dialog, we have got an ability to choose additional official packages for the installation:
Such tools will help in the work on large-scale projects, if you are just starting to learn the framework, you can skip this step for now.
Click Finish and wait a little while CodeLobster downloads the current version of the framework and unpacks it into the designated directory.
When the wizard has finished its work, we will check the correctness of the installation - open the address http://localhost/laravel/public/ in your browser, it is in this folder the public files are stored.
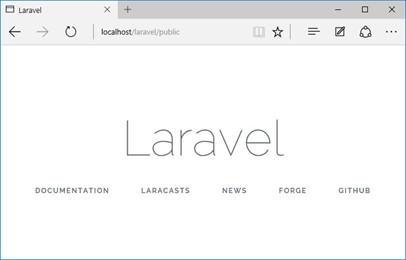
As you can see, the Laravel logo appeared, there are no error messages, which means everything is well.
We can study the structure of the new project on the Project tab, and also edit the main settings of our WEB-application.
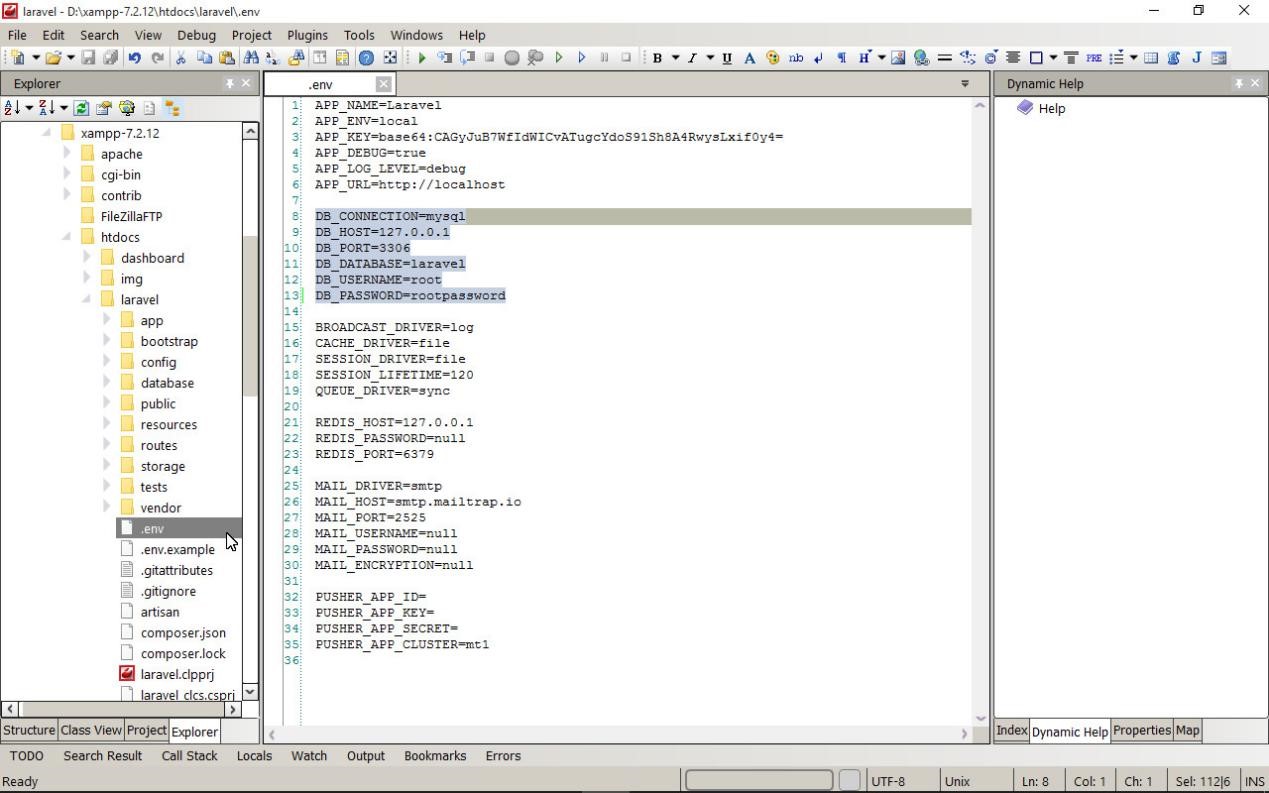
If you are using a database connection, go to the file explorer in the left pane of the IDE and open the .env file in the editor, this file stores the environment variables.
Find the line DB_CONNECTION=mysql and enter the parameters for connecting to MySQL. In our example, this fragment looks like this:
1 | DB_CONNECTION=mysql |
Testing the Work of the Framework
Laravel includes an object-relational mapping (ORM) system, it is called Eloquent and is an implementation of the Active Record design pattern (AR).
The rules for naming classes, tables and their fields are used in order to unify ways of connecting objects and their corresponding tables and rows in the DB.
In the database that we have connected to the current installation, there is a ready-made table on which we can practice.
The name of the table is “countries”, it contains the names of countries and phone codes - these are the “name” and “phonecode” fields.
To use Eloquent, you need to create your own class that extends the “Model” class. Create a file “Country.php” in the “app” folder and add the following lines to it:
1 | <?php |
According to the naming rules, a class called “Country” (in the singular) will represent entries in the table “countries”. This is quite enough for now, the rest of the work for us will be done by the framework.
To take advantage of the model for the data access, let’s create a router - we will link the URL http://localhost/laravel/public/countries to the function of extracting records from the table.
Routers for your WEB applications are stored in the routes folder, open the web.php file in the editor and add a few lines of your own code to it:
1 | Route::get('/countries', function () { |
The IDE understands the structure of the Laravel project very well and provides hints and dynamic help on all the functions and classes included in the framework.
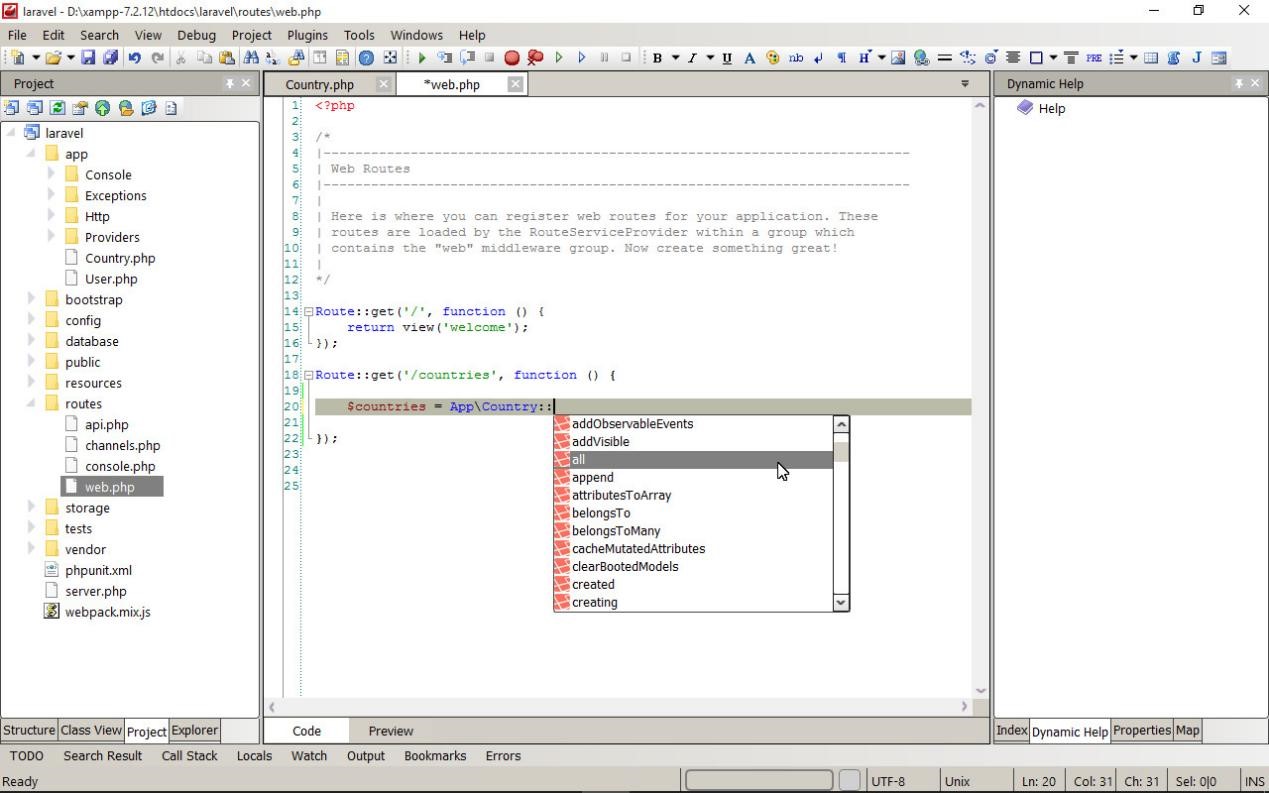
It will be much easier for you to use all its advantages if you use autocomplete while typing by pressing the Ctrl + Space key combination to get the list of methods that are allowed in this context.
When we execute our code, an array with information about countries will be extracted, it can now be passed to the view for formatting and display.
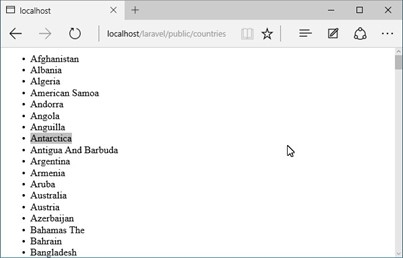
In our educational example, we simply select the names of the countries and create an HTML list, and it will be displayed using the default view.
Open the address http://localhost/laravel/public/countries in the browser and see an accurate list with the names of all countries from our database.
Conclusion
In this article, we have learned how to quickly create a new project and install Laravel using the wizard in CodeLobster IDE.
This is a universal approach - it is suitable for any operating system and does not require the use of the command line or the installation of additional software.
The principle of operation of all MVC and ORM frameworks is the same. After reading this article, you have learned the basic steps to get started with Laravel, with this knowledge you will be able to easily and simply master other PHP libraries.
If you have any issue regarding this post, mention your issue in comment section or reach me through my E-mail.





